Data Analyst vs. Data Scientist: Differences and Similarities in the Data Analysis World

In today's digital era, Big Data and Data Science have revolutionized the way companies and organizations make decisions and gain valuable knowledge for their growth and success. In this scenario, two professional profiles have emerged as prominent players: the Data Scientist and the Data Analyst.
In today's technology-driven world, data is considered one of the most valuable assets for companies. With the increasing amount of data being generated every day, organizations need to have a systematic approach to collecting, analyzing and interpreting this information. This is where data analytics and data science come into play.
Let's clarify the key differences between these profiles, allowing you to better understand which one is best suited for your interests and future IT projects.
What does a Data Analyst do?
Data Analyst (data analyst) are experts in generating reports and dashboards that summarize the results of analysis in a clear and concise manner, making it easy for decision makers to understand.
Education:
Data Analysts generally have at least a bachelor's degree in fields related to computer science, statistics, engineering, or social sciences. It is also common to find Data Analysts with a marketing background, as this allows them to better understand the context and business objectives of their analysis.
Specialization:
Data Analysts specialize in data management and analysis. They acquire skills in the use of data analysis tools such as SQL, Excel, Tableau, Power BI, R or Python.
Years of Experience:
Data Analysts can vary in their experience, from recent graduates to professionals with several years of experience. In general, for entry-level positions, at least 1-2 years of experience in data analysis or related functions may be required, while more senior positions may require 3-5 years or more of experience.

What does a Data Scientist do?
Data Scientists spend their time using analytical tools and techniques to extract knowledge and understand patterns from data, make informed decisions and solve complex problems in a variety of areas, such as business, science, technology, medicine, among others.
Education:
Data Scientists typically have advanced academic training, in fields such as Computer Science, Statistics, Mathematics, Engineering, Physics or related areas. This advanced education provides them with a solid foundation in advanced data analysis and machine learning techniques.
Specialization:
Data Scientists specialize in applying advanced machine learning, artificial intelligence and data mining techniques to solve complex problems and develop predictive models.
They use programming languages such as Python.
Experience:
Data Scientists typically have more years of experience compared to Data Analysts. They may have 3 to 5 years of experience or more in roles related to data analysis, model development and artificial intelligence projects.
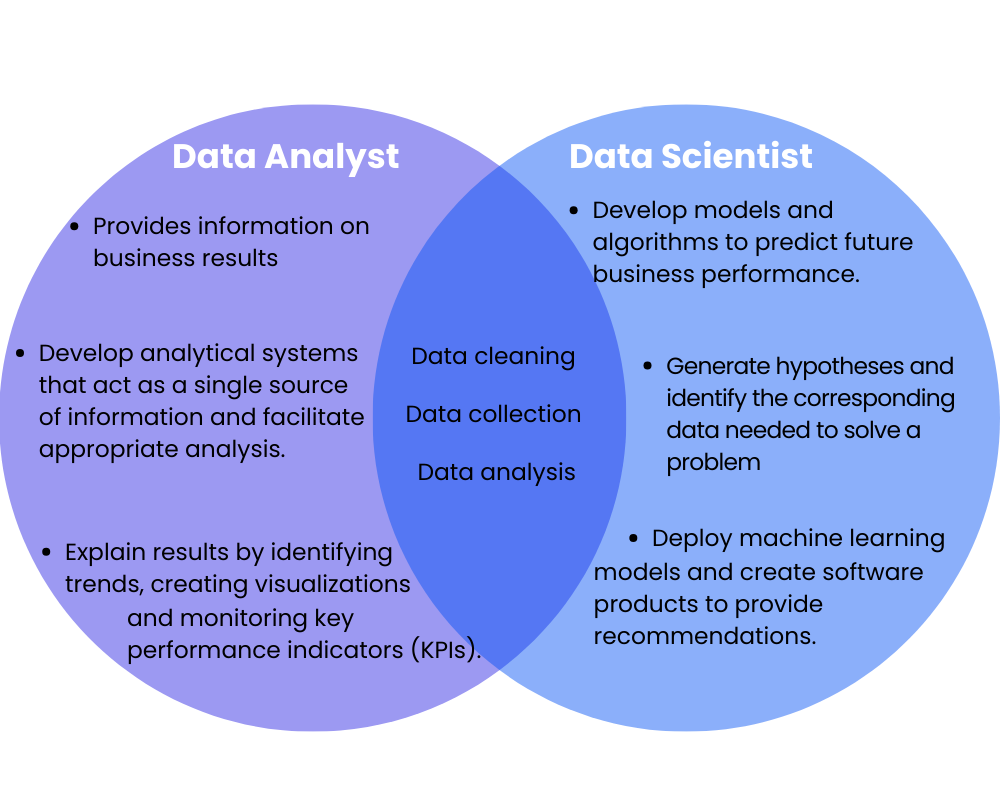
What benefits will you get if you put these two profiles together in your IT projects?
- You will get a highly efficient and versatile workforce in data analysis.
- The collaboration between both profiles would allow you to tackle complex problems in a comprehensive manner. Data Analysts would provide immediate insights and answers to specific data-driven questions, while Data Scientists would develop advanced models for process prediction and optimization, leading to more robust and accurate solutions.
- Combining the skills of both profiles will enable more informed and data-driven decision-making.
- The collaboration between these two profiles will foster innovation and creativity in problem solving.